How Long Does It Take For Myelin Sheath To Repair
Oct. 11, 2022
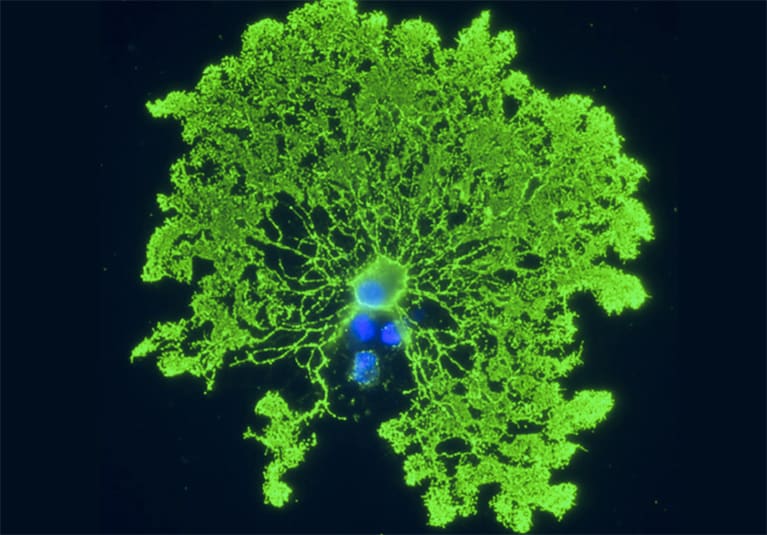
Myelin is essential to the conduction of nerve impulses in the brain and spinal string, and myelin loss is a key pathophysiological component of neurological injury and disease, including multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain and spinal cord injury, stroke, and some neuropsychiatric disorders.
Identifying factors that encourage product of and protect the function of myelin-producing cells — oligodendrocytes and their progenitors (OPCs) — is an important avenue of research aimed at promoting central nervous system (CNS) health.
In a recently published article in Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Molecular Basis of Illness, Isobel A. Scarisbrick, Ph.D., director of the Neuroregeneration and Neurorehabilitation Laboratory at Mayo Clinic'south campus in Rochester, Minnesota, and co-authors investigate the human relationship betwixt fat intake, exercise and myelin product in mice.
The roles that dietary fatty intake and other external factors play in the production of oligodendrocytes and OPCs is non well-understood. Although brain lipids take high fatty content, consumption of a diet containing excess fats and sugars has been shown to be detrimental to CNS function. Withal, myelin associates requires a significant corporeality of lipids, and lipids play an of import role in glial cell myelination.
Do has been shown to have positive effects on CNS office. Recent research has yielded testify that exercise tin modulate the action of diet on the CNS. Boosted animal and human studies have shown that new myelin germination in the brain is required to acquire new skills, whether it's running on an practice cycle or learning to play the piano or juggle.
"Our study was designed to provide a clearer picture of the interaction betwixt high fatty consumption and exercise grooming and their issue on myelin and myelin-forming cells in the developed spinal cord," explains Dr. Scarisbrick.
Study methods
Mayo researchers studied adult mice, randomized into iv experimental groups: Two groups had a sedentary lifestyle and free admission to a regular diet (SRD) or a high-fat diet (SHF). Another ii groups were assigned to either the regular diet (ERD) or the high-fat nutrition (EHF) and had free access to an practice running wheel.
Study findings
After seven weeks, researchers analyzed the lumbosacral spinal cord tissue to measure the furnishings of diet and exercise on several building blocks required for myelin assembly in the 4 study groups, including proteolipid protein (PLP) and myelin basic protein (MBP).
- High-fatty diet in combination with exercise preparation increases myelin protein expression. PLP and MBP levels were highest in the grouping that exercised and consumed a loftier-fat diet. Practice training or high fatty consumption alone also increased PLP. MBP levels in the ERD and the SHF groups were not significantly unlike.
- High-fat diet alone or in combination with exercise has the greatest consequence on myelin-related protein expression. The SHF and EHF groups had the highest levels of PLP RNA. Elevations in PLP RNA induced by a high-fat diet lone (SHF) were significantly greater than those achieved by exercise training alone (ERD).
- Exercise preparation protects against loss of OPCs or mature oligodendrocytes induced by a high-fatty nutrition. The SHF group had thirty to fifty percent fewer OPCs. While exercise alone didn't affect the OPC or oligodendrocyte numbers, mice in the EHF group did non experience OPC loss.
- Exercise grooming in combination with a loftier-fat nutrition positively modulates expression of IGF-I levels. This growth cistron is known to play important roles in OPC proliferation, survival and differentiation. IGF-1 RNA levels were highest in the ERD and EHF groups, suggesting that exercise exerts the greatest influence here.
- Loftier-fat diet in combination with exercise converges on energy biosensing systems to restore mitochondrial function and complimentary radical homeostasis. While SHF mice experienced excessive mitochondrial activity and free radical production, EHF mice upregulated silent mating type information grooming (SIRT1) and the production of free radical scavengers that may protect myelin and myelinating cells from damage in the central nervous system.
These findings suggest that the primal nervous system is capable of adapting to the demands of a loftier-free energy Western diet when afforded aplenty exercise.
"Our results suggest that consuming high levels of saturated fat in conjunction with a sedentary lifestyle tin lead to a reduction in myelin-forming cells. Merely exercise training tin can help reverse this process and promote the myelinogenesis necessary to come across increased energy demands," explains Dr. Scarisbrick.
For more information
Yoon H, et al. Interplay between practice and dietary fat modulates myelinogenesis in the central nervous arrangement. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Molecular Basis of Disease. 2022;1862:545.
Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/medical-professionals/physical-medicine-rehabilitation/news/analyzing-the-role-of-diet-and-exercise-in-myelin-production/mac-20429394

0 Response to "How Long Does It Take For Myelin Sheath To Repair"
Post a Comment